NDG has worked closely with the Cisco CCNA lab team to develop CCNA Exploration 1 labs. CCNA Exploration 1 is supported by the Network Fundamentals Pod (NFP). NFP is a pod specifically designed for the CCNA 4.0 Exploration 1 course. The supported lab list (below) highlights the labs that are compatible with NFP. Nov 15, 2020 1.6.1 Packet Tracer – Implement a Small Network Answers Packet Tracer – Implement a Small Network (Answers Version) Answers Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the Answers copy only. This activity requires some knowledge of how to build topologies in Packet Tracer. You may want to quickly train students Continue reading. Packet Tracer Network CCNA Security labs. CCNA Security labs can be downloaded for Packet Tracer versions starting from 6.1 as this version was the first to feature an ASA 5505 Firewall.These labs allow students to practice clientless SSL VPN, site to site VPN, and firewalling with deep packet inspection feature.
12.1.9 Packet Tracer – Identify Packet Flow Answers
Packet Tracer – Identify Packet Flow(Answers Version)
Answers Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only.

In this activity, you will observe packet flow in a LAN and WAN topology. You will also observe how the packet flow path may change when there is a change in the network topology.
Part 1: Verify Connectivity

Part 2: Remote LAN Network Topology
Part 3: WAN Network Topology
Packet Tracer allows the design and creation of a simulated networking topology. In this activity, you are presented with a simplified topology to observe packet flow. You will explore how packets travel through the network using the simulation mode in Packet Tracer. You will also observe the changes in packet flow when there is a change in the network topology.
- Latest version of Packet Tracer installed
Part 1:Verifying Connectivity
In this part, you will verify that you can access the other networks from devices on the Home Network.
- Click PC0. Select the Desktop tab and open the Web Browser.
- In the URL field, enter www.cisco.pka and press Go. Be sure to use the .pka domain, not the .com domain. It should be successful. You can click Fast Forward Time to speed up the process.
- Repeat this for www.web.pka. It should be successful.
- Exit the web browser when finished.
Part 2:Remote LAN Network Topology
In this part, you will use the simulation mode in Packet Tracer to observe how packets flow through a remote LAN network.
- Switch to Simulation mode (Shift + S). Click Show All/None to clear all the selected event list filters.
- Click Edit Filters. Select DNS under the IPv4 tab and HTTP under Misc tab.
- Open a web browser on PC0. Enter www.web.pka and press Go.
Question:
Predict the packet path to resolve www.web.pka to an IP address. Record your prediction.
Type your answers here.
DNS packets: PC0 > Wireless Router0 > Cable Modem0 > Cloud0 > Router5 > East > Switch0 > Switch1 > Public DNS and reverse the path back to the originator PC0.
- Click Capture / Forward until the webpage is displayed on PC0 to view the packet flow. Click View Previous Events when prompted by the Buffer Full dialog box.
Question:
After the IP address has been resolved, which path did HTTP packets travel to display the webpage? Record your observations.
Type your answers here.
DNS packets: PC0 > Wireless Router0 > Cable Modem0 > Cloud0 > Router5 > East > Switch0> Switch1 > Switch2 > www.web.pka and reverse the path back to the originator PC0.
- Switch to Real time mode (Shift + R). Click the X icon in the right tool panel to select the Delete tool. Remove the link between Switch0 and Switch 1 from the Public Network to simulate a broken link. After 30 seconds, the network will learn of the broken link. You can click Fast Forward to speed up the process.
- Select the Arrow tool above the Delete tool to de-select Delete.
- Switch to Simulation mode (Shift + S). Open a web browser in Tablet0 and navigate to www.web.pka. You can click Auto Capture/Play to have Packet Tracer forward the packets without your interaction. You can also move the Play Slider to the right to speed up the packet forwarding.
Question:
With a broken link in the LAN, how did the path change? Record your observation.
Type your answers here.
It went through Switch 0 > Switch2 > Switch1 to reach Public DNS server.
Part 3:WAN Network Topology
Step 1:PC0 to websites.
- Remaining in Simulation mode, open a web browser on PC0. Enter www.cisco.pka and press Go.
Question:
Predict the packet path to resolve www.cisco.pka to an IP address. Record your prediction.
Need driver sony dpp-fp50 for mac. Type your answers here.
DNS packets: PC0 > Wireless Router0 > Cable Modem0 > Cloud0 > Router5 > East > Switch0 >Switch2 > Switch1 > Public DNS and reverse the path back to the originator PC0.
- Click Capture / Forward until the webpage is displayed on PC0 to view the packet flow. Click View Previous Events when prompted by the Buffer Full dialog box.
Ccna Lab Simulator
Question:
After the IP address has been resolved, which path did HTTP packets travel to display the webpage? Record your observations.
Type your answers here.
DNS packets: PC0 > Wireless Router0 > Cable Modem0 > Cloud0 > Router5 > Router2> Router4 > West >Switch > www.cisco.pka and reverse the path back to the originator PC0.
- Switch to Real time mode (Shift + R). Remove the link between Router4 and Router2 from the topology to simulate an inaccessible path. The routers are using Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) to dynamically adjust routing tables to account for the deleted link.
- Switch to Simulation mode (Shift + S). Open a web browser in Tablet0 and navigate to www.cisco.pka.
Question:
With a broken link in the WAN, how would the path change? Record your observation.
Type your answers here.
It will go through Router2 > Router1 or Router3 > Router4 to www.cisco.pka.
- Switch to Real time mode (Shift + R).
Step 2:PC1 to websites.
- Click PC1 > Desktop and open a command prompt.
- Enter tracert www.web.pka at the command.
PC> tracert www.web.pka
Tracing route to 209.165.202.132 over a maximum of 30 hops:
11 ms1 ms0 ms192.168.0.1
20 ms0 ms4 ms209.165.200.225
32 ms1 ms0 ms192.0.2.2
42 ms1 ms2 ms192.0.2.18
52 ms3 ms2 ms192.0.2.26
66 ms3 ms2 ms209.165.202.132
710 ms7 ms11 ms209.165.202.132
Trace complete.
- Match the IP addresses in the tracert results to the devices in the topology. Hover over the routers in the topology to view the IP addresses of the interfaces on the routers. If the popup does not stay active long enough, you can access router IP addresses in the following manner: Click the router > CLI > press Enter. Now enter the command show ip interface brief to getting a listing of the interfaces and IP addresses.
Trace Number | Device | Interface | IP Address |
West | GigabitEthernet 0/1 | 192.168.0.1 | |
2 | Router4 | Serial 0/1/1 | 209.165.200.225 |
3 | Router3 | Serial 0/0/0 | 192.0.2.2 |
4 | Router2 | Serial 0/0/1 | 192.0.2.18 |
5 | Router5 | Serial 0/1/1 | 192.0.2.26 |
6 | East | Serial 0/0/0 | 209.165.202.130 |
7 | www.web.pka | NIC | 209.165.202.132 / 192.168.2.254 |
Network address translation (NAT) is used to translate the private www.web.pka IP address of 192.168.2.254 to a routable IPv4 address of 209.165.202.132. In the tracert result, the first line of IPv4 address of 209.165.202.132 is for the G0/1 interface of East. The second line of IPv4 address of 209.165.202.132 displays the public IPv4 address of the web server.
- Switch to Simulation mode (Shift + S). Open the web browser on PC1 and enter www.web.pka as the URL. Click Go.
- Click Capture / Forward to load the web page.
Question:
Compare the tracert results to the simulation results for the HTTP packets. Record your observations.
Type your answers here.
The tracert and simulation results both show the same path to the web server.
Last Updated on March 14, 2018 by
1.1.1.8 Packet Tracer – Using Traceroute to Discover the Network
Packet Tracer – Using Traceroute to Discover the Network (Answer Version)
Answer Note: Red font color or Gray highlights indicate text that appears in the Answer copy only.
Topology
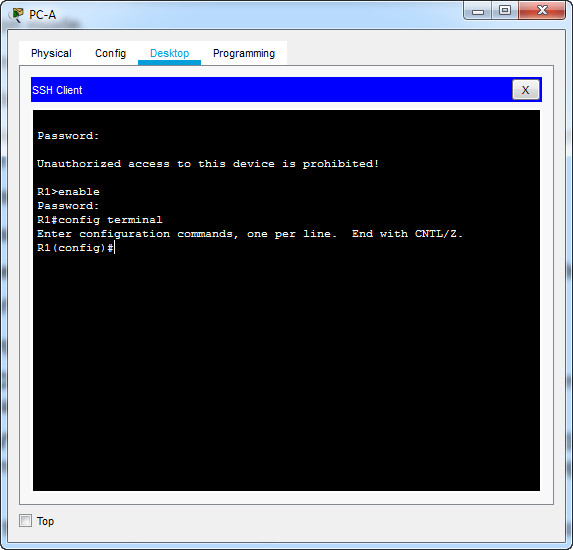
1.1.1.8 Packet Tracer – Using Traceroute to Discover the Network
Scenario
The company you work for has acquired a new branch location. You asked for a topology map of the new location, but apparently one does not exist. However, you have username and password information for the new branch’s networking devices and you know the web address for the new branch’s server. Therefore, you will verify connectivity and use the tracert command to determine the path to the location. You will connect to the edge router of the new location to determine the devices and networks attached. As a part of this process, you will use various show commands to gather the necessary information to finish documenting the IP addressing scheme and create a diagram of the topology.
Note: The user EXEC password is cisco. The privileged EXEC password is class.
Trace and Document a Remote Location
Note: As you complete the following steps, copy command output into a text file for easy reference and record the missing information in the Addressing Scheme Documentation table.
Refer to the Hints page for a review of the commands used. In Packet Tracer, click the right arrow (>) on the bottom right side of the instruction window. If you have a printed version of the instructions, the Hints Roland va 76 zip drive software. page is the last page.
- Click Sales and the Desktop tab > Command Prompt. Use the ipconfig command to check the IP address configuration for Sales.
- The new server web address is b2server.pt.pka. Enter the following nslookup command to discover the IP address for b2server:
- PC> nslookup b2server.pt.pka
- What address did the command return for b2server? 128.107.64.254
- Enter the tracert command to determine the path from Sales to b2server.pt.pka.
- PC> tracert b2server.pt.pka
- Telnet to the first IP address in the tracert output and log in.
- PC> telnet 172.16.0.1
- You are connected to the R4 router. Issue the traceroute command on the router using the address for b2server determined in step b. What is different about the traceroute command on the router compared to tracert on the PC? There is one less hop since the command is originating from R4, the order of the fields in the output is different listing the IP address in the first column.
- What is the significance of R4 to Sales? It is the default gateway for Sales.
- Use the show ip interface brief command to display the status of the interfaces on R4. Based on the output of the command, which interface is used to reach the next device in the list output from the tracert command? Interface S0/0/0 is connected to the 64.100.150.0 network.
- Hint: Use show running-config to view the subnet mask values for the interfaces.
- Telnet to the second IP address in the tracert list and log in. You can use the number in the far left column of the tracert output to track where you are in the list. What is the name of the device to which you are connected? Tier3a
- Issue the show ip route command and study the output. Referring to the list of codes at the beginning of the output, what are the different types of routes displayed in the routing table? D – EIGRP, C – Connected, L – local, S – static
- Based on the show ip route command output, which interface is the exit interface for the next IP address listed in your original tracert output? GigabitEthernet0/0
- Telnet to the third IP address in the tracert list and log in. What is the hostname of the current device? ISP-Tier3b
- Issue the show ip route connected command. What networks are connected directly to this router? 64.100.8.0/24, 64.104.222.0/30, 64.104.222.4/30, 128.107.46.0/24
- Refer to the Addressing Scheme Documentation table. Which interfaces connect the devices between trace route 2 and trace route 3? GigabitEthernet 0/0 for ISP-Tier3a and GigabitEthernet0/1 for ISP-Tier3B
- Telnet to the fourth IP address in the tracert list and log in. What is the name of the device? B2-R1
- Issue a command to determine to what interface b2server.pt.pka is connected. Student could use show ip route, show ip interface brief or show run.
- If you have used the Addressing Scheme Documentation table as you completed the previous steps, the table should now be complete. If not, finish the table now.
- With a complete documentation of the addressing scheme and knowledge of the path from Sales to branch2.pt.pka, you should be able to now draw the new branch location in the Topology Documentation space below.
Ccna Labs Pdf
Addressing Scheme Documentation
| Trace Route ID | Device | Interface | Address | Subnet Mask |
| – | Sales | NIC | 172.16.0.x (DHCP) | 255.255.255.0 |
| 1 | R4 | G0/0 | 172.16.0.1 | 255.255.255.0 |
| S0/0/0 | 64.100.150.1 | 255.255.255.252 | ||
| S0/0/1.1 | 64.100.200.1 | 255.255.255.252 | ||
| 2 | ISP-Tier3a | G0/0 | 64.104.222.1 | 255.255.255.252 |
| G0/1 | 64.104.223.1 | 255.255.255.252 | ||
| S0/0/0 | 64.100.100.2 | 255.255.255.252 | ||
| S0/1/0 | 64.100.150.2 | 255.255.255.252 | ||
| 3 | ISP- Tier3b | G0/1 | 64.104.222.2 | 255.255.255.252 |
| G0/2 | 64.100.8.1 | 255.255.255.0 | ||
| F0/1 | 128.107.46.1 | 255.255.255.0 | ||
| F/0/2 | 64.104.222.5 | 255.255.255.252 | ||
| 4 | B2-R1 | G0/0 | 64.104.222.6 | 255.255.255.252 |
| G0/1 | 128.107.64.1 | 255.255.255.0 | ||
| 5 | b2server.pt.pka | NIC | 128.107.64.254 | 255.255.255.0 |
Topology Documentation
Use the space below to draw the topology for the new branch location.
Answer Only: Branch2 Topology
Suggested Scoring Rubric
| Activity Section | Possible Points | Earned Points |
| Questions (2 points each) | 20 | |
| Addressing Scheme Documentation | 60 | |
| Topology Documentation | 20 | |
| Total Point | 100 |
Hints – Command Summary Reference
DOS Commands
ipconfig – The output of the default command contains the IP address, network mask and gateway for all physical and virtual network adapters.
ipconfig /all – This option displays the same IP addressing information for each adapter as the default option. Additionally, it displays DNS and WINS settings for each adapter.
Nslookup – Displays information that you can use to diagnose Domain Name System (DNS) infrastructure.
Syntax:
nslookup dns.name
Ccna Lab 1.6.1 Pka Completed Pdf
Tracert – Determines the path taken to a destination by sending Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) Echo Request messages to the destination with incrementally increasing Time to Live (TTL) field values. The path displayed is the list of near-side router interfaces of the routers in the path between a source host and a destination. The near-side interface is the interface of the router that is closest to the sending host in the path. Used without parameters, tracert displays help.
Syntax:
tracert [TargetName/IP Address]
IOS Commands
show ip interface – Displays the IP interface status and configuration
show ip interface brief – Displays a brief summary of IP status and configuration
show ip route – Displays the full IP routing table
show ip route connected – Displays a list of active directly connected networks
show running-config – Displays the current operating configuration
traceroute – Trace route to destination